Novel synthesis of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by linear sweep voltammetry: Study of structural, morphological and optical properties
4.8 (795) In stock

This work reports on the structural, morphological and optical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films grown by co-electrodeposition of different Cu, Sn and Zn elements using linear sweep voltammetry and cyclic voltammetry techniques. The obtained films were sulfurized in N2 atmosphere at 550°C for 1h. SEM analysis shows a very dense and uniform surface with large particles. X-ray diffraction patterns exhibit the kesterite structure of CZTS with the preferred orientation of the (112) plan. Raman spectroscopy measurements confirm the XRD results with clear peaks at 253, 289, 339 and 368 cm−1. In addition, the Raman shift was attributed to CZTS kesterite mode vibration. The band gap of CZTS film is found to be close to 1,48eV.

XRD pattern for the Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticle. The peaks have been

PDF) Single–step electrodeposition of a microcrystalline Cu< sub

Hassan KIROU, laboratory of materials and renewable energy, University Ibn Zohr - Agadir, Agadir, Physics

Abdeslam Elfanaoui's research works University Ibn Zohr - Agadir, Agadir and other places

Khalid BOUABID, Phd, University Ibn Zohr - Agadir, Agadir, Faculty of Sciences
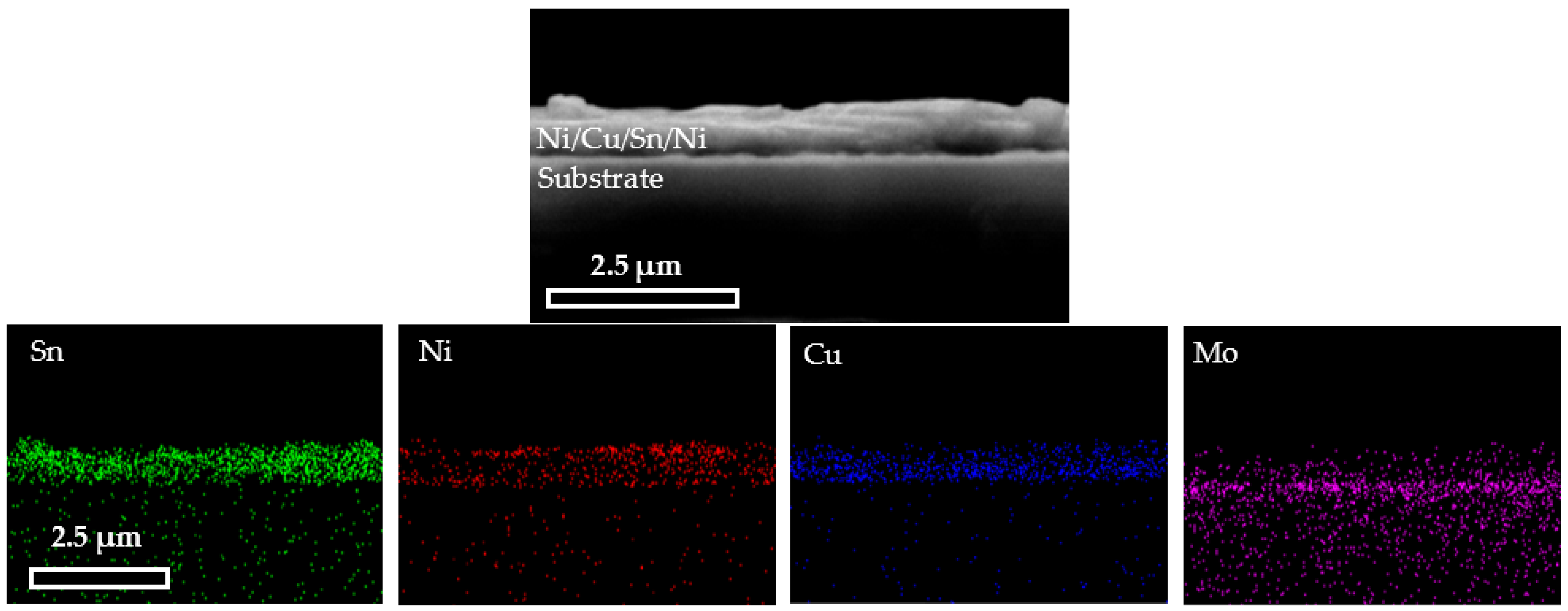
Coatings, Free Full-Text

Abdelkader OUTZOURHIT, Professor, PhD, applied physics, Cadi Ayyad University, Marrakesh, UCAM, Department of Physics

Effect of complexing agents on the electrodeposition of Cu-Zn-Sn metal precursors and corresponding Cu2ZnSnS4-based solar cells

PDF) Copper electrodeposition onto zinc for the synthesis of

Single-step electrodeposition of CZTS thin film: Influence of

Chemical synthesis of Cd1-x-yZnxCuySzSe1-z composite thin films
Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) plot of the highest conducting
Linear Sweep Voltammetry Setup Parameters
Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) - PalmSens
 GetUSCart- DIBAOLONG Womens Yoga Pants Wide Leg Comfy Drawstring Loose Straight Lounge Running Workout Legging Gray Brown XL
GetUSCart- DIBAOLONG Womens Yoga Pants Wide Leg Comfy Drawstring Loose Straight Lounge Running Workout Legging Gray Brown XL One Piece Strawhat Pirates Gang Mouse Pad Gaming Mouse Pad – Anime Town Creations
One Piece Strawhat Pirates Gang Mouse Pad Gaming Mouse Pad – Anime Town Creations Loose Fit Hoodie - Light pink - Men
Loose Fit Hoodie - Light pink - Men eden on X: I gave Kate a massive wedgie and ripped her knickers
eden on X: I gave Kate a massive wedgie and ripped her knickers What's The Scoop On The BODIMAX Sleeves?
What's The Scoop On The BODIMAX Sleeves?- AE Stretch Curvy Ripped Straight Jean
