When you are given two sides of a right triangle, how do you find the third side?
4.8 (546) In stock
Using the Pythagorean theorem which applies exclusively to right-angled (or right) triangles. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides adjacent to the right angle. The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle. Hence, using the figure as a guide: a^2+b^2=c^2 If you know any two of the three variables above (a, b, and c), the third can be easily calculated.
How to find an unknown side of a right triangle using trigonometry and the law of sines if we have all three angles and two sides - Quora

The Pythagorean Theorem
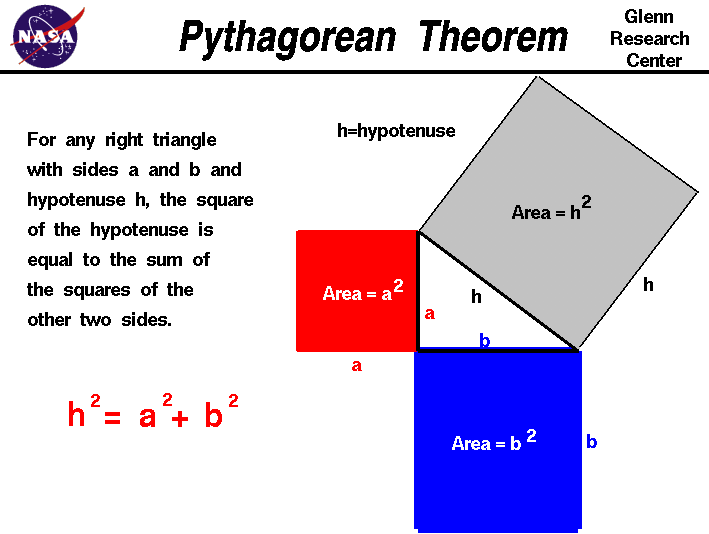
Pythagorean Theorem

10.1: Non-right Triangles - Law of Sines - Mathematics LibreTexts

Find the missing side (side a) of the right triangle ABC

Non-right triangle trig

Area of a triangle

How to find incentre of a right angled triangle
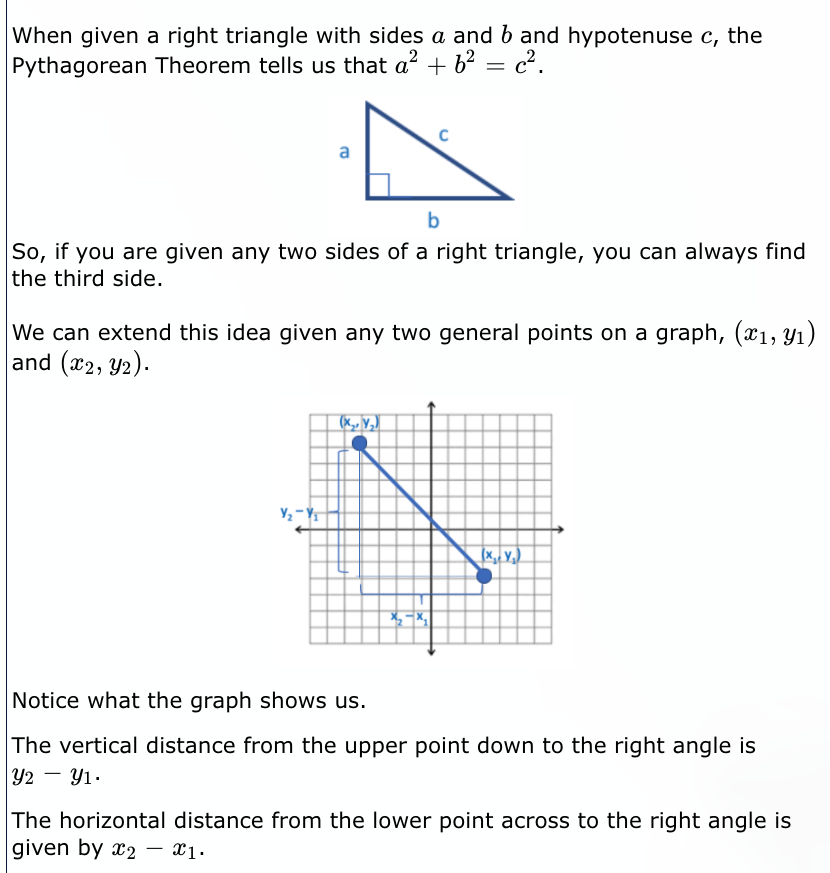
Solved When given a right triangle with sides a and b and

3.03 Sides and angles of right-angled triangles, Year 12 Maths, Australian Curriculum 12 Essential Mathematics - 2020 Edition


⏩SOLVED:Find the range for the measure of the third side of a…

cos) You hove given a trigagle with two slos of equal leght
Hypotenuse of a Right Triangle, Steps & Examples - Lesson
Special right triangles review (article)
 Veronika, initiator and co-founder of RUSH Initiative and SOUND UP festival — ArtyGeneration
Veronika, initiator and co-founder of RUSH Initiative and SOUND UP festival — ArtyGeneration Watch Big Natural Tits Bouncing Up & Down #178 - Big Ass, Big Tits, Titty Fuck Porn - SpankBang
Watch Big Natural Tits Bouncing Up & Down #178 - Big Ass, Big Tits, Titty Fuck Porn - SpankBang- From the archives - @sommerray for @shopsommerray collection
 Women's Winter Warm One Yard Korean Fashion Cotton Linen Skirt
Women's Winter Warm One Yard Korean Fashion Cotton Linen Skirt Victoria Secret Lingerie Black Satin Lace Cami Set, XS - NEW
Victoria Secret Lingerie Black Satin Lace Cami Set, XS - NEW Comprar Pantalón chándal mujer azul Pantalones fitness de mujer
Comprar Pantalón chándal mujer azul Pantalones fitness de mujer
