PDF] Two Simple yet Accurate Equations for Calculating the Fugacity Coefficient Phi and the Gas Compressibility Factor
4.7 (680) In stock

Two Simple yet Accurate Equations for Calculating the Fugacity Coefficient Phi and the Gas Compressibility Factor Z . by A.E. for mychemengmusings.wordpress.com In this post two new powerful equations are presented one for the Gas Compressibility Factor ‘Z’ and one for the Gas Fugacity Coefficient ‘phi’. Both give excellent prediction results for the sub-critical reduced pressure region and superheated vapor region. These two equations are surprisingly simple, allow direct calculation without the need for iterations hence easy to implement in spreadsheets or used on handheld devices and calculators! The two form a thermodynamically consistent pair. Three Charts have been prepared mapping out the predictions made with these equations. Numerical calculation examples are given including for superheated Steam, Ethane, Propane and Propylene. The basis for each of these equations is presented in Part III of this post giving ample attention to the basis on which these equations rest and their validation against measured data.

PDF] Two Simple yet Accurate Equations for Calculating the Fugacity Coefficient Phi and the Gas Compressibility Factor

DOC) Computation of the Compression Factor and Fugacity Coefficient of Real Gases

SOLVED: Problem 2. This problem involves the derivation of the fugacity-coefficient formula (1), where T.P is the fugacity and Z=y is the compressibility factor of the material at temperature T and pressure

Why is fugacity, or z, always less than 1? - Quora

Fugacity, Activity, Thermo Graphs, PDF, Gases

The 'Lewis line': A proposed new ideal curve of fluids - ScienceDirect
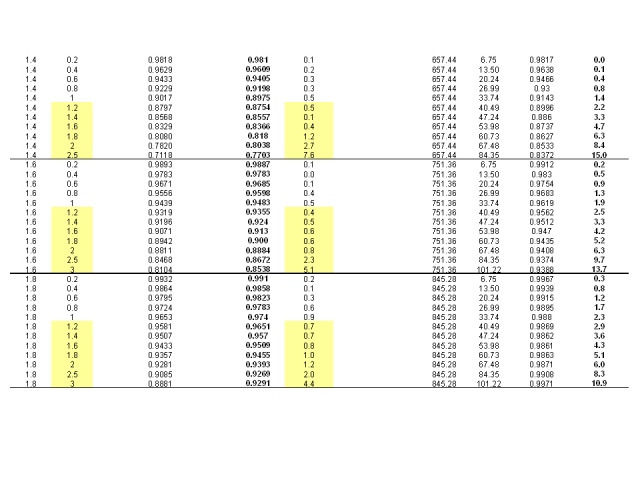
Fugacity Coefficient Phi vs Pr Chart

Understanding Fugacity and Fugacity Coefficients Through Detailed Mathematical Derivations and Explanations, PDF, Equations

A compositional model for CO2 flooding including CO2 equilibria between water and oil using the Peng–Robinson equation of state with the Wong–Sandler mixing rule

Functional-Segment Activity Coefficient Equation of State: F-SAC-Phi

The solubility of H2 in NaCl brine at high pressures and high temperatures: Molecular simulation study and thermodynamic modeling - ScienceDirect

Solubility of vitamin A in supercritical CO2: experimental study and thermodynamic modeling

DOC) Computation of the Compression Factor and Fugacity Coefficient of Real Gases

Modeling of CO2 Freeze-Out in the Processing of CO2-Rich Natural Gas
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior Chemistry: Atoms First
Compressibility factor (Z) for a van der Waals real gas at
The given graph represent the variations of Z Compressibility
 Adidas: Online Sales Growth & Leading Product Segments
Adidas: Online Sales Growth & Leading Product Segments- Discount Blouses, Shirts & Tanks, Women's Clearance Tops
- Faux Suede Flare Pants
- História do Johny Bravo, o chefão da Rocinha atualmente #rocinha #roci
 MELENECA Women's Unlined Strapless Bra with Underwire Minimizer for Large Busts Seamless Jacquard Fabric Black 32E
MELENECA Women's Unlined Strapless Bra with Underwire Minimizer for Large Busts Seamless Jacquard Fabric Black 32E Old Navy Printed Boxer-Briefs Underwear 7-Pack for Boys
Old Navy Printed Boxer-Briefs Underwear 7-Pack for Boys


